Seeking strategies to enhance your company’s competitiveness? On our blog, we’ve delved into digital transformation, e-commerce, and the array of advantages a digitalized enterprise can harness in terms of efficiency and market edge.

In this discussion, we’re focusing on a specific tool: the SKU code. This is a tracking system employed by businesses to monitor their inventory levels.
This tool enables a company to maintain a thorough overview of its stock, streamline efficiency and delivery schedules, scrutinize sales patterns, and recommend items to online shoppers. Essentially, the SKU code is crucial for operating efficiently and effectively.
Here’s an in-depth look at what an SKU code is and its mechanism.

Defining the SKU Code
The SKU, standing for Stock Keeping Unit, is a distinct alphanumeric identifier assigned to products for inventory tracking. Unlike a barcode, which is universal, the SKU code is tailored for internal use.
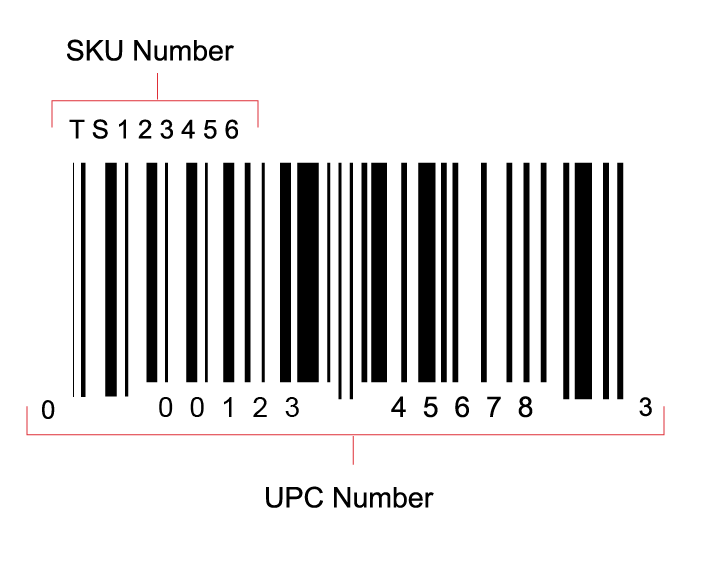
This identifier usually reflects key product details organized by priority based on the business’s needs. For instance, the sequence could start with characters denoting a price range, followed by gender, size, brand, etc.
An SKU code might also denote an item’s location, indicating whether it’s stored in a warehouse or displayed in a store, meaning a single product could have multiple SKUs based on its placement within the business.
In summary:
- An SKU code is an alphanumeric tag linked to a product.
- It’s not universal but internal to the company.
- Each SKU is unique within the organization.
- A product can have various SKUs over its lifecycle depending on its location.
Utilizing an SKU Code
E-commerce entities extensively use SKU codes, but they offer any business a detailed snapshot of inventory right down to the smallest saleable unit.
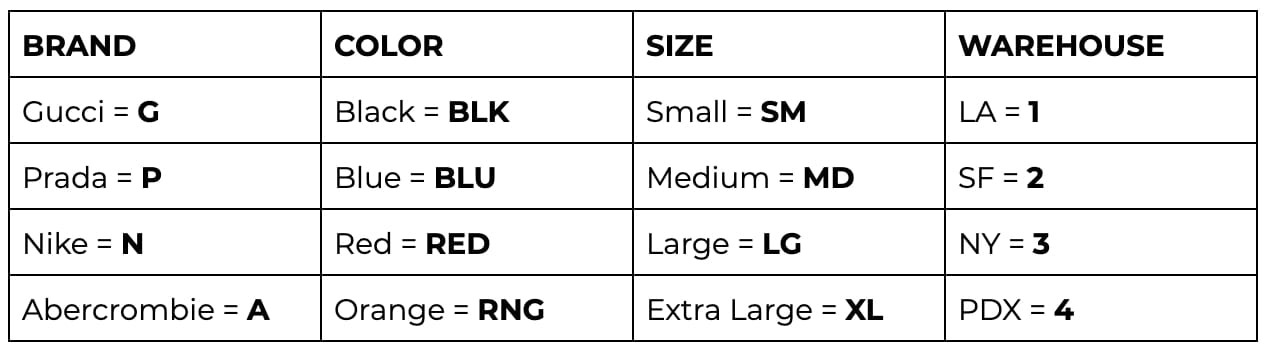
For example, a red Nike sweatshirt in small size stocked in Los Angeles might have an SKU like N-RED-SM-1.
The structure of an SKU code depends on the company’s strategy and requirements. Before crafting one, consider the essential tracking elements and their importance order. For instance, if color is a frequent customer query, place this at the start of your SKU for easy reference.
The code’s length should reflect inventory size. For a small, single-brand inventory, tracking might focus solely on product type, possibly following a structure like:
Type-Size-Color
Additional product information that could be identified by an SKU includes:
- Color
- Size
- Gender
- Price range
- Style
- Brand
- Item number
- Category code
- Storage location
Essentially, the SKU’s composition should align with the company’s strategic vision and needs. If starting from scratch, take the time to carefully plan its implementation.
Creating an SKU Code
For minimal inventories, SKU codes can be manually created using Excel or online generators. For more complex operations—a business with thousands of products across multiple locations—it’s advisable to automate SKU assignment via a POS system, which manages sales transactions.
Tips for crafting an SKU code include:
- Keeping it between 8 and 12 characters long.
- Avoiding initial zeros to prevent scanning errors.
- Steering clear of letters that resemble numbers, like O and I.
- Incorporating only strategically significant information.
- Making the format intuitive, e.g., TAS101 for a wired keyboard, TAS102 for wireless.
Differentiating SKU and UPC Codes

A common error is confusing SKU codes with other product identifiers like the Universal Product Code (UPC). However, they serve different purposes:
SKU Code vs. Bar Code (UPC):
- Alphanumeric vs. Numeric with a barcode
- Variable length vs. 12 digits
- Internal inventory tracking vs. Universal product identification
- Company-specific product traits vs. Product and manufacturer identification
- Free vs. Fee-based
Therefore, it’s crucial to distinguish between these codes to avoid confusion.
Advantages of SKU Codes for Businesses:
- Precise inventory tracking: SKU codes optimize stock management, allowing for proactive product category replenishment and efficient shelf restocking.
- Trend monitoring: Data analysis reveals best-selling products, informing marketing strategies and inventory decisions.
- Improved logistics: SKU codes clarify product locations, facilitating organized and cost-effective shipping.
- E-commerce recommendations: Online shops use SKU codes for automated product suggestions, enhancing the shopping experience.

In essence, adopting SKU codes exemplifies digitalization’s role in bolstering competitiveness and market readiness for businesses of all sizes.
Are you prepared to implement it?